Hotel guest data quality management: The audit methodology that reveals hidden revenue leaks
We show how to audit hotel guest data quality through email validation, duplicate detection, system consistency and actionable segmentation. An essential step to maximise direct bookings and prevent revenue leakage.
Most hotel marketing teams operate under the assumption that their guest databases represent comprehensive coverage of past visitors, but systematic audits consistently reveal that fewer than 25% of actual guests can be effectively reached through email campaigns.
We like to introduce these articles with practical examples based on the experiences hotel groups share with us in meetings.
A few days ago, the Marketing Director of a national hotel group told us he was confident that their database represented complete coverage of past guests. They had implemented WiFi captive portals across all properties, maintained detailed property management system records, and regularly exported guest information to their customer relationship management platform. When the board requested metrics on direct booking campaign effectiveness, the initial analysis seemed encouraging: 180,000 email addresses collected over eighteen months, with campaigns generating steady booking activity.
The breakthrough came when they conducted their first systematic database audit using third-party verification services and cross-property data analysis. Of those 180,000 email addresses, 67,000 failed basic validation tests for syntax errors, invalid domains, or spam trap detection. Another 23,000 represented duplicate records where the same guests appeared multiple times across different properties or booking channels. Most revealing, when they mapped email collection against actual guest stays recorded in their property management systems, they discovered their database represented contact information for just 23% of guests who had stayed during the audit period.
The remaining 77% of guests had been lost to a combination of manual collection errors, system integration gaps, and verification failures that accumulated over time. The revenue impact was substantial: their email campaigns were reaching fewer than one in four past guests, missing direct booking opportunities worth an estimated €1.8 million annually based on their average conversion rates and guest lifetime value calculations.
This scenario illustrates why hotel guest data quality management requires systematic audit methodologies rather than assumptions about database completeness and accuracy.
The compound effect of informal data collection

Most hotel groups collect guest information through multiple touchpoints without systematic quality controls that ensure data accuracy and completeness.
- Front desk staff manually record email addresses during check-in processes, often introducing transcription errors or accepting obviously fake addresses to expedite guest service.
- WiFi captive portals capture authentication information without validating guest identity against property management records, allowing unauthorized users network access while missing opportunities to enrich guest profiles with verified contact data.
The technical architecture at most properties operates in silos that prevent comprehensive data validation and enrichment. Captive portal systems function independently from property management platforms, with no real-time communication to verify guest identity or detect data entry errors. Customer relationship management systems receive exported data through manual processes that introduce delays and inconsistencies, preventing real-time verification and correction of invalid information.
These informal processes create compound quality problems that worsen over time:
- Invalid email addresses accumulate in marketing databases, creating bounce rates that damage sender reputation and reduce deliverability for all subsequent campaigns.
- Duplicate guest records multiply across properties and booking channels, fragmenting guest profiles and preventing comprehensive view of guest behavior and preferences.
- Missing companion guest information creates blind spots where marketing teams cannot reach significant portions of their actual guest population.
A other property European resort chain discovered these compound effects when analyzing their email campaign performance across different collection sources.
Addresses collected through manual front desk processes showed bounce rates of 41%, compared to just 7% for direct booking confirmations and 3% for loyalty program enrollments. The difference reflected the absence of verification protocols in their manual collection processes, while their booking systems included basic syntax checking and loyalty programs required email confirmation before activation.
The Seven-Point Database Health Assessment Framework
Systematic hotel guest data quality management starts with comprehensive auditing that measures current performance across multiple dimensions of accuracy, completeness, and usability. The **Seven-Point Database Health Assessment** gives marketing teams clear criteria and benchmarks to uncover hidden quality problems that affect campaign effectiveness and direct booking performance.
1. Email Validity
This is the foundation of any quality audit. It verifies collected addresses against multiple checks to determine deliverability potential. It includes syntax validation (formatting errors), domain validation (fake or expired domains), MX record checks (server readiness), and disposable email detection. In hotels relying on manual collection, **20–45% of addresses typically fail these tests**, while those with real-time verification achieve success rates above **94%**.
2. Completeness
Completeness measures what percentage of actual guests appear in the marketing database with usable contact information. This requires mapping email capture against PMS records to identify missing contacts. Leading hotel groups with integrated captive portals achieve **70–80% completeness**, while properties depending on manual collection often fall below **25%**.
3. Duplicates
Duplicate records distort guest profiles and limit the ability to analyze booking behavior or communication preferences. The audit must quantify duplicate rates and trace their causes, which are usually manual entry errors, poor system integration, or weak deduplication protocols. Advanced systems reduce duplicate rates from **15–20% down to less than 2%**.
4. Consistency Across Systems
Data must be consistent across PMS, CRM, WiFi portals, and booking engines. Without integration, discrepancies and delays undermine accuracy and make records unreliable. Automated synchronization improves consistency, ensures accuracy in real time, and eliminates the errors introduced by manual exports and imports.
5. Consent Documentation
Compliance with GDPR and similar regulations requires a clear record of how and when consent was obtained. Without proper consent tracking, marketing databases risk being legally vulnerable and unusable for commercial campaigns. Audits must confirm that consent is systematically captured and stored.
6. Data Freshness
Databases decay quickly as guest emails change over time. Freshness assessments measure how much of the database is still active and valid. Regular verification prevents high bounce rates, maintains sender reputation, and ensures that marketing campaigns reach real guests instead of outdated addresses.
7. Practical Usability
Finally, audits should confirm that the database supports effective segmentation and personalization. Having “clean” data is not enough — the information must be actionable for campaigns. Usability means being able to target guests based on preferences, behavior, and demographics, which drives higher engagement and direct bookings.
Diagnostic Tools for Marketing Teams
Marketing teams conducting database quality assessments need specific diagnostic tools that quantify performance problems and prioritize improvement initiatives based on revenue impact. These tools should provide actionable insights that support business cases for database improvement investments while establishing baseline metrics for measuring optimization success.
Campaign deliverability analysis connects database quality problems to marketing performance outcomes, measuring how invalid addresses and poor data quality affect email campaign effectiveness. The analysis should track bounce rates, spam folder placement, and sender reputation metrics across different collection sources and time periods. Marketing teams can use this analysis to quantify the revenue impact of database quality problems and justify investments in verification systems and data governance processes.
Hotels with systematic email verification achieve deliverability rates above 99%, compared to industry averages of 85% to 90% for properties without verification protocols. The difference translates directly to campaign reach and conversion potential, with verified databases typically generating 15% to 25% higher response rates due to improved inbox placement and sender reputation.
Guest reachability assessment measures what percentage of past guests can be effectively targeted through email campaigns, accounting for invalid addresses, unsubscribe rates, and consent documentation. This metric provides a realistic view of marketing database utility and helps teams understand the true scope of their direct booking potential. The assessment should segment reachability by guest demographics, booking channels, and property types to identify opportunities for targeted improvement initiatives.
Revenue impact modeling connects database quality metrics to direct booking performance, calculating the opportunity cost of missing guest contacts and invalid email addresses. The modeling should consider average guest lifetime value, booking conversion rates, and campaign frequency to estimate the revenue potential of database improvement initiatives. This analysis provides marketing teams with specific ROI calculations that support investment decisions and performance measurement.
A property hotel group used revenue impact modeling to demonstrate that database quality improvements could generate an additional €2.3 million in direct bookings annually. The analysis showed that increasing their guest database completeness from 31% to 73% would enable them to reach 42% more past guests with targeted campaigns, while improving email verification would increase campaign deliverability from 78% to 99%.
Quality Scoring and Prioritization Matrix
Effective hotel guest data quality management requires systematic prioritization of improvement initiatives based on implementation complexity and revenue impact potential. The Quality Scoring and Prioritization Matrix helps marketing and IT teams focus resources on initiatives that deliver the highest return on investment while building foundations for long-term database excellence.
High-impact, low-complexity initiatives typically focus on implementing real-time email verification at existing collection points, particularly WiFi captive portals and direct booking systems. These implementations prevent poor-quality data from entering marketing databases without requiring major system changes or operational process modifications. Real-time verification typically improves email deliverability by 15% to 25% within 90 days of implementation, providing immediate return on investment through improved campaign performance.
Medium-impact, medium-complexity initiatives involve establishing automated integration between property management systems and customer relationship management platforms to eliminate manual data export and import processes. These integrations improve data accuracy and completeness while reducing operational overhead for marketing teams. Automated PMS-CRM synchronization typically increases guest database completeness by 20% to 40% while improving data accuracy from typical rates of 67% to above 94%.
High-impact, high-complexity initiatives focus on comprehensive captive portal integration that captures companion guest information and implements sophisticated verification protocols across all collection touchpoints. These implementations require significant technical development and operational process changes but deliver the most substantial improvements in database completeness and quality. Comprehensive integration typically increases guest database completeness from industry averages of 15% to 25% up to 70% to 80% while achieving email verification success rates above 94%.
The prioritization matrix should also consider regulatory compliance requirements and risk mitigation factors that may elevate the priority of certain initiatives regardless of immediate revenue impact. GDPR compliance requirements for consent documentation and data retention may necessitate governance improvements that support long-term marketing effectiveness even if they don’t deliver immediate campaign performance benefits.
Stopping Bad Data at the Door: What Real-Time Gates Actually Check
Real-time verification systems implement multiple validation layers that operate in sequence during guest data collection, each checking different aspects of email address validity and deliverability potential. Understanding these verification mechanisms helps marketing teams evaluate system capabilities and set appropriate quality thresholds that balance data accuracy with guest experience requirements.
Syntax validation (RFC 5322)
Syntax validation operates as the first verification layer, checking email address formatting against RFC 5322 standards for structure and character usage. This validation identifies addresses missing required elements like the at symbol, improper domain formatting, or unacceptable character combinations that would prevent message delivery. Syntax validation typically completes within 10 to 20 milliseconds and catches 15% to 25% of invalid addresses in hotel environments, primarily due to typos and transcription errors from manual data entry processes.
Domain validation (DNS)
Domain validation forms the second verification layer, confirming that email domains exist and maintain proper DNS records for receiving messages. This process queries domain name servers to verify domain registration and mail exchange record configuration, identifying fake domains, expired registrations, and configuration errors that would prevent message delivery. Domain validation requires 50 to 150 milliseconds depending on DNS response times and catches an additional 8% to 12% of invalid addresses that pass syntax validation.
MX Record Verification / SMTP Connection
Mail exchange record verification establishes SMTP connections with domain mail servers to confirm infrastructure readiness for receiving email communications. This validation identifies domains with misconfigured mail servers, temporary outages, or deliberate blocking of external connections that would prevent campaign delivery. MX record verification operates without sending actual messages, protecting guest privacy while ensuring deliverability potential.
Disposable Email Detection
Disposable email detection screens addresses against databases of known temporary email services and identifies patterns associated with disposable address generation. This validation protects hotels from collecting email addresses that expire within hours or days, ensuring marketing campaigns can reach guests weeks or months after their initial stay. Disposable email detection typically identifies 5% to 15% of addresses collected through hotel WiFi systems, where guests are most likely to use temporary addresses to avoid ongoing marketing communications.
Spam Traps and Blacklists
Spam trap and blacklist screening identifies email addresses associated with anti-spam organizations, security services, or known problematic domains that could trigger spam complaints or blacklist additions. This validation protects hotel sender reputation by preventing campaigns from reaching addresses that could damage deliverability across all marketing communications. Spam trap detection is particularly important for hotels because sender reputation problems affect deliverability for all campaigns, not just individual messages.
The Data Hygiene Ladder: Collect, Validate, Enrich, Govern
Systematic hotel guest data quality management operates through four progressive stages that transform raw guest information into verified, actionable marketing assets. The Data Hygiene Ladder provides a framework for understanding how data quality improvements build upon each other to create comprehensive database excellence that supports sophisticated marketing campaigns and regulatory compliance requirements.
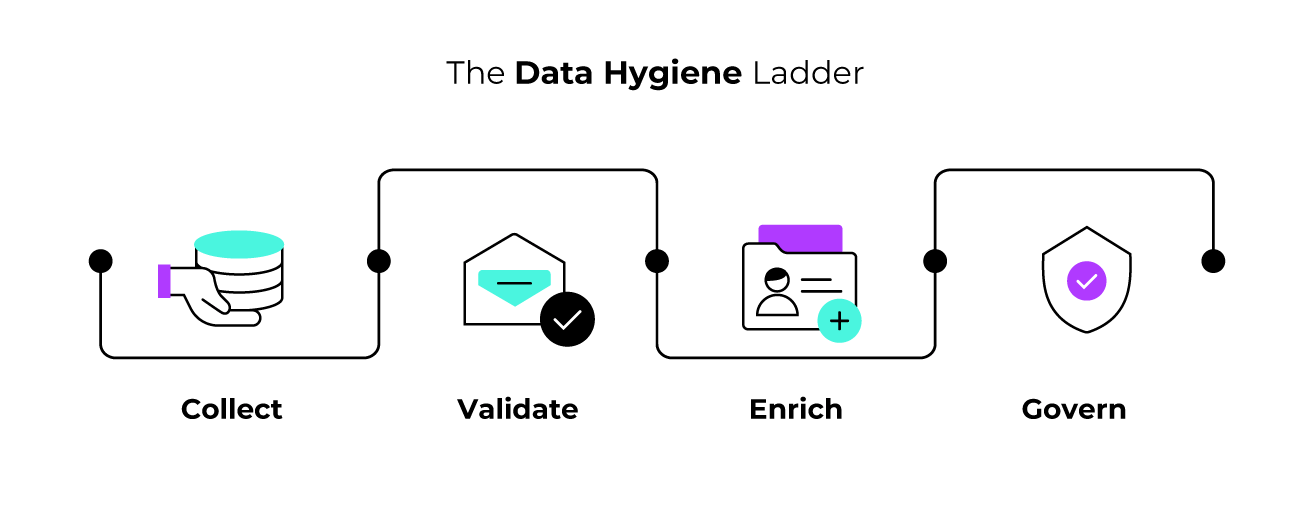
- Collection optimization focuses on capturing guest information through integrated systems that validate identity and enrich profiles automatically. Advanced captive portal implementations communicate directly with property management systems to verify guest identity against booking records while collecting companion information that traditional methods miss entirely. This integration typically increases total guest data capture by 40% to 60% beyond the primary booking contact, filling gaps where companions don’t provide check-in information but connect to WiFi networks during their stay.
- Validation implementation establishes real-time verification protocols that prevent poor-quality data from entering marketing databases and damaging sender reputation. Comprehensive verification systems check syntax formatting, domain validity, disposable email detection, and spam trap screening within 200 to 500 milliseconds of data entry, providing immediate feedback that allows guests to correct errors before completing authentication processes. Hotels implementing real-time verification achieve email deliverability rates above 99%, compared to industry averages of 85% to 90% for properties without verification protocols.
- Enrichment automation connects guest data across multiple touchpoints to create comprehensive profiles that support sophisticated segmentation and personalization strategies. Automated systems capture booking channel attribution, property preferences, spending patterns, and communication behavior while maintaining consent documentation and GDPR compliance requirements. This enrichment process enables marketing teams to deliver targeted campaigns based on demonstrated guest interests rather than generic demographic categories.
- Governance establishment creates systematic frameworks for data retention, consent management, and quality maintenance that ensure long-term database utility and regulatory compliance. Automated deduplication algorithms identify and merge duplicate guest records, while retention policies archive or anonymize information according to regulatory requirements. Comprehensive audit trails document data collection sources, consent capture mechanisms, and access control effectiveness to support regulatory compliance demonstrations.
A 12-hotel group that implemented the complete Data Hygiene Ladder saw dramatic improvements in both operational efficiency and marketing performance within six months. They reduced manual data export and import processes from 40 hours weekly to zero while improving data accuracy from 67% to 94%. Their email deliverability increased from 78% to 99%, and campaign open rates improved from 18% to 62% due to better list quality and enhanced personalization capabilities.
Hotel groups seeking to transform their guest database performance through systematic hotel guest data quality management should focus on implementing real-time email verification at all collection points to prevent poor-quality data from entering marketing systems and damaging sender reputation. This single initiative typically improves campaign deliverability by 15% to 25% within 90 days while establishing the technical foundation for more comprehensive database optimization efforts.
Marketing teams should conduct systematic database health assessments using the seven-point framework to quantify current performance and prioritize improvement initiatives based on revenue impact potential. The audit methodology reveals hidden quality problems that compound over time, enabling data-driven decisions about system investments and operational process improvements that transform guest databases from cost centers into strategic marketing assets.