5 factors to consider before installing 5G in a hotel.
Before making potential changes to your infrastructures, we recommend carrying out a technical audit and analysing the following points in your property.
The arrival of 5G technology is generating many doubts in our industry, as it represents a significant change to the infrastructures of many properties.
Above all, owners are worried about adapting cables and network equipment, as well as redirecting investments, because they would need to install a large number of antennae or receptors in order for 5G to work in every possible area of the property.
Although properties expect to have to invest a large amount of money to install 5G, doing so would bring about many advantages, including, but not limited to, offering guests a top quality service.
Before making potential changes to the infrastructures, owners should first get a specialised company to carry out a technical audit, monitoring the current state of the network and suggesting improvements.
Our team of experts has come up with the 5 main points that you ought to check to prepare your property for the arrival of 5G:
1. New construction vs existing building
When we talk about a new construction or complete reform, the costs and material associated with the installation of telecommunications are normally included in the total budget and the impact of these seems relatively minor.
In the next article we will show you some practical cases where each of these types of property and what they involve is presented in graphical form. In the proposals, intake ducts for telecommunications operators, channelling for each room, wiring for fibre optic, dividers throughout the building, reserved spaces which are suitable for equipment rooms, Inferior Telecommunications Installation Area, and Data Processing Centre, etc, are often included.
When we are dealing with an existing building, we first need to check the existing installation. We have to consider whether we need to refurbish the hotel, with minor reform work, or whether we want to improve the state of the rooms or complete another type of reform and take advantage of this to carry out or improve the existing cabling.
2. Type of existing cabling
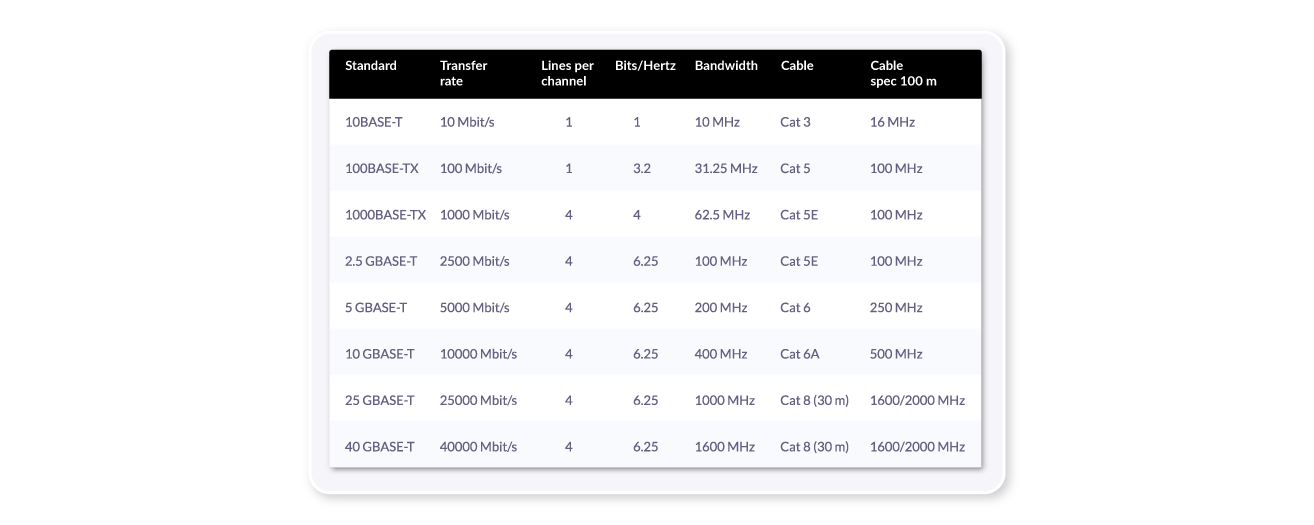
If we are talking about copper pair wiring, UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) the most typical is represented in this table. This type of electric cable allows for optimum IT system performance. Without a doubt, this type of cabling is best accepted, as it is not excessively expensive and is easy to install. However, at high speed, it is vulnerable to electromagnetic interference in the environment. We have to check which type of cable we have, because in some cases, it may now be obsolete.
If we have fibre optic, this is better, because it allows for higher speeds and increased distances when sending data. This is currently the most commonly used type of cable across the world as it is immune to electromagnetic interference.
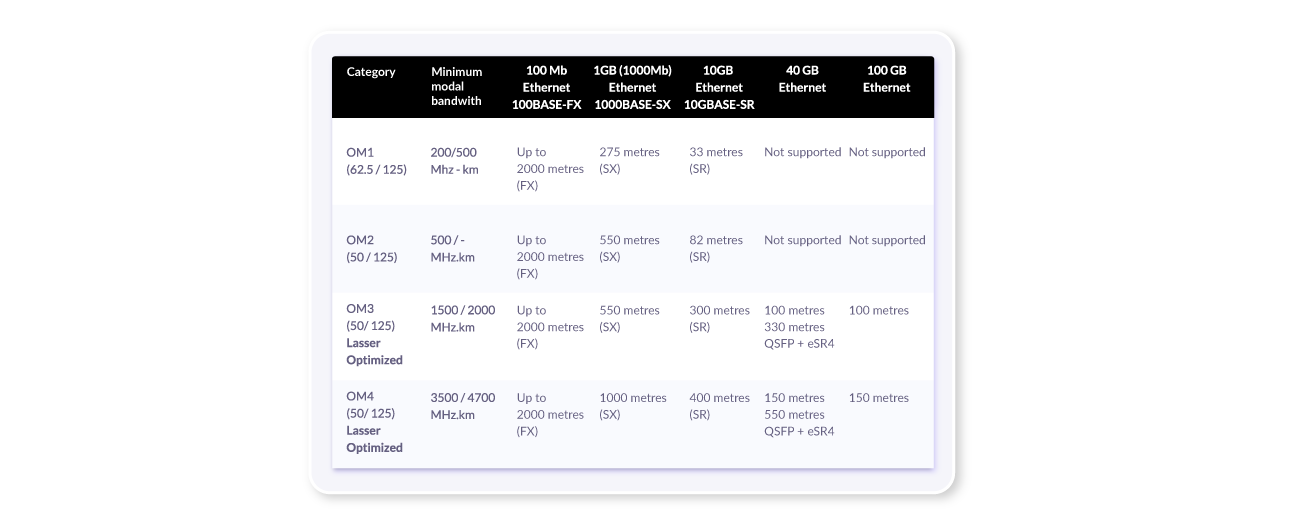
In an initial analysis, we must therefore confirm which type of cable is being used, and then use the tables to decide which category it belongs to. Most often, we find UTP and Fibre. Fibre allows us to have longer distances and higher speeds, so it is recommended as a link between distribution points and the copper pairs (UTP) allowing us to electrically feed the access points (PoE) using the same cable.
3. State of each point
We must check the state and performance of each point in the network: see whether it has been affected by loss, attenuation, noise, state of the connectors, state of the electric input PoE (Power over Ethernet), etc.
4. Distances to points on the network and between distribution points
The distance between distribution points (vertical cabling) and from each distribution point to its points of access (horizontal cabling).
In other words, vertical cabling includes the connectors which join rooms, floors, and other areas of the hotel between buildings, where relevant. There will be different switch cabinets or points of distribution which must be interconnected.
Horizontal cabling connects one of the switch cabinets with the connection points located in a same area or zone (a floor or conference room, etc)
5. Certification of the entire set-up
With all this information, we can study the viability of our property and know what performance will be like. Depending on the services that we wish to offer, and the requirements of these, we must make more or fewer changes and improvements.
We won’t always be able to have a new fibre installation with access points in each room, and this is not necessary to adapt to 5G or Wi-Fi 6.
IEEE 802.3bz is a new standard technology which can be used to achieve speeds in the network of 2.5 Gbps and 5 Gbps on copper twisted pair cabling, allowing properties in the 5 and 6 category to use new Wi-Fi 6 or 5G equipment, for example. While not ideal, this is something that many properties with obsolete cabling can adapt to.
But we must understand that not all cat5e or cat6 cabling infrastructures will admit 2.5/5GBASE-T at 100 metres, and we will have to check to ensure compliance.
Being up to date with Wi-Fi installations will mean that the change will seem less traumatic. In the majority of cases, we can take advantage and both technologies can co-exist, because the use cases may require both.
In the next article we will go into more detail and explain everything that it is possible to install in a property.